
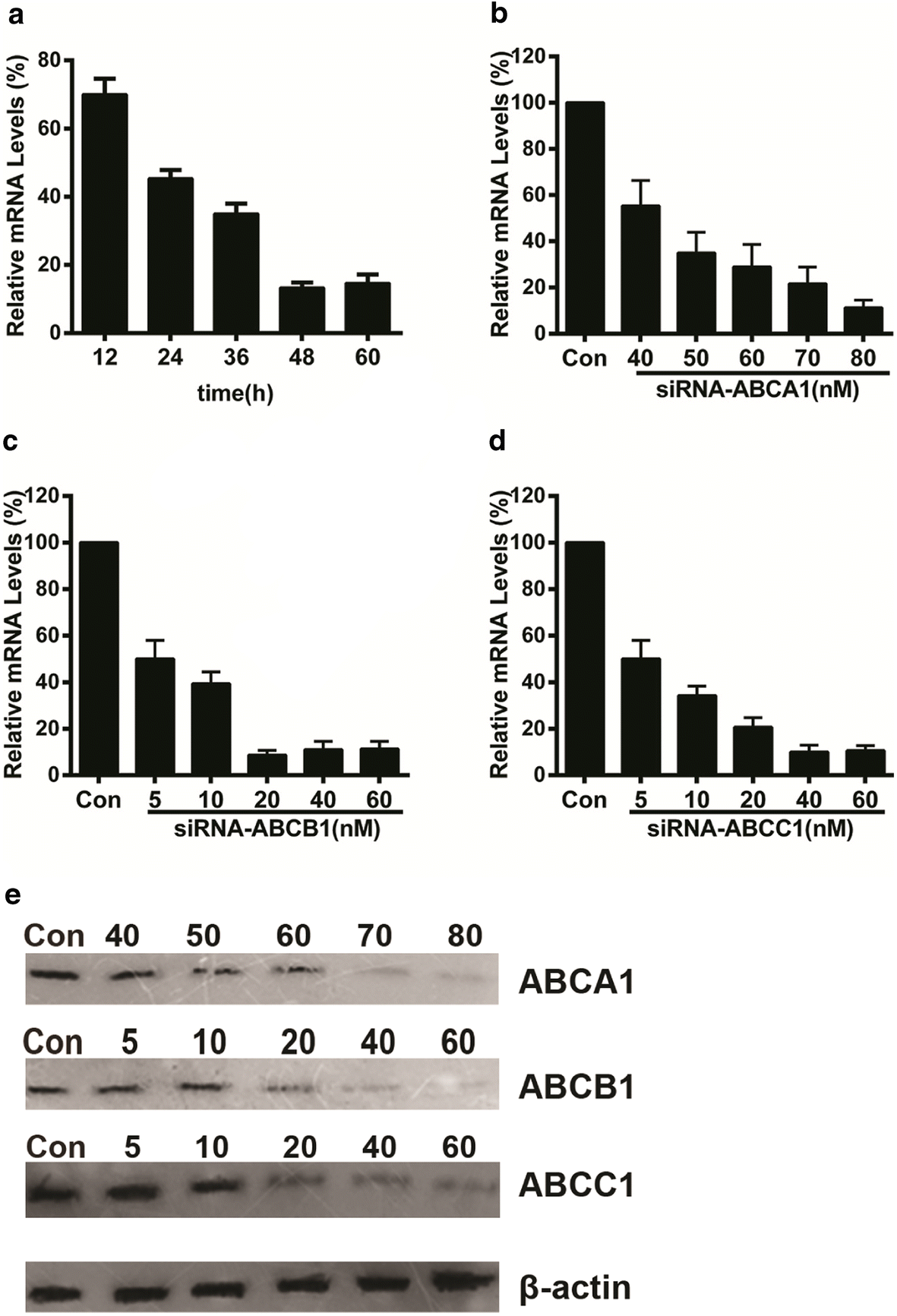
Arsenic is one of the most widespread global environmental toxicants associated with endemic poisoning. ATP-binding cassette (ABC) proteins are transmembrane channels that transport and dispose of lipids and metabolic products across the plasma membrane. The majority of ABC family members (including ABCB1 and ABCC1) are reported to play a role in the development of arsenic and drug resistance in mammals. Previously, we established a human arsenic-resistant ECV-304 (AsRE) cell line and identified ABCA1 as a novel arsenic resistance gene. In the current study, we further investigated the potential contribution of ABCA1, ABCB1, and ABCC1 to arsenic resistance through measurement of survival rates and arsenic accumulation in AsRE cells with RNA interference. The arsenic resistance capacity of ABCC1 was the strongest among the three genes, while those of ABCA1 and ABCB1 were similar. Double or triple gene knockdown of ABCA1, ABCB1, and ABCC1 via RNA interference led to a decrease significant in arsenic resistance when ABCA1/ABCB1 or ABCB1/ABCC1 were simultaneously silenced. Interestingly, no differences were evident between cells with ABCA1/ABCC1 and ABCC1 only knockdown. Our findings suggest that ABCA1 and ABCB1 proteins display similar arsenic resistance capabilities and possibly coordinate to promote arsenic resistance in AsRE cells.
电邮:xuxl@hznu.edu.cn
电话:0571-28861723
邮编:311121
地址:浙江省杭州市余杭区仓前余杭塘路2318号
Copyright © 2021 杭州师范大学徐晓玲课题组 公安备案号:33011002011919 浙ICP备11056902号-1 技术支持:亿校云
地址:浙江省杭州市余杭塘路2318号
邮编:311121
电邮:xuxl@hznu.edu.cn 电话:0571-28861723
版权所有 © 2021 杭州师范大学徐晓玲课题组
公安备案号:33011002011919
浙ICP备11056902号-1
技术支持:亿校云